#Java String to Int
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Java String to Int: A Comprehensive Guide for Developers
Introduction to Java String to Int: In the world of Java programming, converting strings to integers is a common task that developers encounter frequently.
Whether you're parsing user input, manipulating data from external sources, or performing calculations, understanding how to convert strings to integers is essential.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the various techniques, best practices, and considerations for converting strings to integers in Java.
Understanding String to Int Conversion:
Before diving into the conversion process, it's important to understand the difference between strings and integers in Java.
Strings are sequences of characters, while integers are numeric data types used to represent whole numbers. The process of converting a string to an integer involves parsing the string and extracting the numerical value it represents.
Using parseInt() Method:
One of the most common methods for converting strings to integers in Java is the parseInt() method, which is part of the Integer class. This method takes a string as input and returns the corresponding integer value. It's important to note that parseInt() can throw a NumberFormatException if the string cannot be parsed as an integer, so error handling is essential.
Example:
String str = "123"; int num = Integer.parseInt(str); System.out.println("Integer value: " + num);
Handling Exceptions:
As mentioned earlier, the parseInt() method can throw a NumberFormatException if the string is not a valid integer.
To handle this exception gracefully, developers should use try-catch blocks to catch and handle the exception appropriately. This ensures that the application doesn't crash unexpectedly if invalid input is provided.
Using valueOf() Method:
In addition to parseInt(), Java also provides the valueOf() method for converting strings to integers. While value Of() performs a similar function to parseInt(), it returns an Integer object rather than a primitive int. This can be useful in certain situations where an Integer object is required instead of a primitive int.
Example:
String str = "456"; Integer num = Integer.valueOf(str); System.out.println("Integer value: " + num);
Considerations and Best Practices:
When converting strings to integers in Java, there are several considerations and best practices to keep in mind:
Always validate input strings to ensure they represent valid integers before attempting conversion.
Handle exceptions gracefully to prevent application crashes and improve error handling.
Use parseInt() or valueOf() depending on your specific requirements and whether you need a primitive int or Integer object.
Consider performance implications, especially when dealing with large volumes of data or performance-critical applications.
Conclusion:
Converting strings to integers is a fundamental task in Java programming Language, and understanding the various techniques and best practices is essential for developers.
By following the guidelines outlined in this comprehensive guide, you'll be well-equipped to handle string to int conversion efficiently and effectively in your Java projects.
Happy coding!
#java#Java String to Int#how to convert string to int in java#how to convert string to int in java example#how to convert a string to int in java#how to convert string to integer in java#convert string to int java#convert string to int in java#how can convert string to int in java#how to convert a string to integer in java#convert int to string in java#string to integer in java#java convert string to int#convert string to int#how to convert integer to string in java#string to int java
1 note
·
View note
Text
bitch java is so fucking annoying why does the S in String need to be capitalized but the i in int has to be in lowercase??? why do you need to import a whole ass module just to take an input from the user??? why are all the commands so fucking long and hard to remember??? JUST DIE
138 notes
·
View notes
Text
int main (string args[]) {
hi! i can't believe nobody has created this account yet!
but anyway... ever wished your java had more segfaults and undefined behavior?
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The C Programming Language Compliers – A Comprehensive Overview
C is a widespread-purpose, procedural programming language that has had a profound have an impact on on many different contemporary programming languages. Known for its efficiency and energy, C is frequently known as the "mother of all languages" because many languages (like C++, Java, and even Python) have drawn inspiration from it.
C Lanugage Compliers

Developed within the early Seventies via Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs, C changed into firstly designed to develop the Unix operating gadget. Since then, it has emerge as a foundational language in pc science and is still widely utilized in systems programming, embedded systems, operating systems, and greater.
2. Key Features of C
C is famous due to its simplicity, performance, and portability. Some of its key functions encompass:
Simple and Efficient: The syntax is minimalistic, taking into consideration near-to-hardware manipulation.
Fast Execution: C affords low-degree get admission to to memory, making it perfect for performance-critical programs.
Portable Code: C programs may be compiled and run on diverse hardware structures with minimal adjustments.
Rich Library Support: Although simple, C presents a preferred library for input/output, memory control, and string operations.
Modularity: Code can be written in features, improving readability and reusability.
Extensibility: Developers can without difficulty upload features or features as wanted.
Three. Structure of a C Program
A primary C application commonly consists of the subsequent elements:
Preprocessor directives
Main function (main())
Variable declarations
Statements and expressions
Functions
Here’s an example of a easy C program:
c
Copy
Edit
#include <stdio.H>
int important()
printf("Hello, World!N");
go back zero;
Let’s damage this down:
#include <stdio.H> is a preprocessor directive that tells the compiler to include the Standard Input Output header file.
Go back zero; ends this system, returning a status code.
4. Data Types in C
C helps numerous facts sorts, categorised particularly as:
Basic kinds: int, char, glide, double
Derived sorts: Arrays, Pointers, Structures
Enumeration types: enum
Void kind: Represents no fee (e.G., for functions that don't go back whatever)
Example:
c
Copy
Edit
int a = 10;
waft b = three.14;
char c = 'A';
five. Control Structures
C supports diverse manipulate structures to permit choice-making and loops:
If-Else:
c
Copy
Edit
if (a > b)
printf("a is more than b");
else
Switch:
c
Copy
Edit
switch (option)
case 1:
printf("Option 1");
smash;
case 2:
printf("Option 2");
break;
default:
printf("Invalid option");
Loops:
For loop:
c
Copy
Edit
printf("%d ", i);
While loop:
c
Copy
Edit
int i = 0;
while (i < five)
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
Do-even as loop:
c
Copy
Edit
int i = zero;
do
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
while (i < 5);
6. Functions
Functions in C permit code reusability and modularity. A function has a return kind, a call, and optionally available parameters.
Example:
c
Copy
Edit
int upload(int x, int y)
go back x + y;
int important()
int end result = upload(3, 4);
printf("Sum = %d", result);
go back zero;
7. Arrays and Strings
Arrays are collections of comparable facts types saved in contiguous memory places.
C
Copy
Edit
int numbers[5] = 1, 2, three, 4, five;
printf("%d", numbers[2]); // prints three
Strings in C are arrays of characters terminated via a null character ('').
C
Copy
Edit
char name[] = "Alice";
printf("Name: %s", name);
8. Pointers
Pointers are variables that save reminiscence addresses. They are powerful but ought to be used with care.
C
Copy
Edit
int a = 10;
int *p = &a; // p factors to the address of a
Pointers are essential for:
Dynamic reminiscence allocation
Function arguments by means of reference
Efficient array and string dealing with
9. Structures
C
Copy
Edit
struct Person
char call[50];
int age;
;
int fundamental()
struct Person p1 = "John", 30;
printf("Name: %s, Age: %d", p1.Call, p1.Age);
go back 0;
10. File Handling
C offers functions to study/write documents using FILE pointers.
C
Copy
Edit
FILE *fp = fopen("information.Txt", "w");
if (fp != NULL)
fprintf(fp, "Hello, File!");
fclose(fp);
11. Memory Management
C permits manual reminiscence allocation the usage of the subsequent functions from stdlib.H:
malloc() – allocate reminiscence
calloc() – allocate and initialize memory
realloc() – resize allotted reminiscence
free() – launch allotted reminiscence
Example:
c
Copy
Edit
int *ptr = (int *)malloc(five * sizeof(int));
if (ptr != NULL)
ptr[0] = 10;
unfastened(ptr);
12. Advantages of C
Control over hardware
Widely used and supported
Foundation for plenty cutting-edge languages
thirteen. Limitations of C
No integrated help for item-oriented programming
No rubbish collection (manual memory control)
No integrated exception managing
Limited fashionable library compared to higher-degree languages
14. Applications of C
Operating Systems: Unix, Linux, Windows kernel components
Embedded Systems: Microcontroller programming
Databases: MySQL is partly written in C
Gaming and Graphics: Due to performance advantages
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Java
Eines meiner ersten Codes die ich in Java geschrieben habe, war das hier:
public class JunusVideo { public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Mulder"; String beruf = "Programmierer";
gruss(19);
System.out.println("Ich heiße " + name + " und Arbeite als " + beruf + "."); }
public static void gruss(int hour) {
if (hour < 12) { System.out.println("Guten Morgen!"); } else if (hour < 18) { System.out.println("Guten Tag!"); } else { System.out.println("Guten Abend!"); } } }
Das erste was ich getippt habe und verstanden habe. Ich war sehr stolz darauf. :) Vor allem, weil ich ihn etwas anders gemacht hatte, als im Tutorial und sehr stolz darauf war.
Apropos Tutorial, gelernt habe ich von Junus auf Youtube. Tolle Videos. Sehr einfach erklärt. Kann ich jedem wärmstens ans Herz legen, der erst einsteigt.
youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
LDAP testing & defense
LDAP Injection is an attack used to exploit web based applications that construct LDAP statements based on user input. When an application fails to properly sanitize user input, it's possible to modify LDAP statements through techniques similar to SQL Injection.
LDAP injection attacks are common due to two factors:
The lack of safer, parameterized LDAP query interfaces
The widespread use of LDAP to authenticate users to systems.
How to test for the issue
During code review
Please check for any queries to the LDAP escape special characters, see here.
Automated Exploitation
Scanner module of tool like OWASP ZAP have module to detect LDAP injection issue.
Remediation
Escape all variables using the right LDAP encoding function
The main way LDAP stores names is based on DN (distinguished name). You can think of this like a unique identifier. These are sometimes used to access resources, like a username.
A DN might look like this
cn=Richard Feynman, ou=Physics Department, dc=Caltech, dc=edu
or
uid=inewton, ou=Mathematics Department, dc=Cambridge, dc=com
There are certain characters that are considered special characters in a DN. The exhaustive list is the following: \ # + < > , ; " = and leading or trailing spaces
Each DN points to exactly 1 entry, which can be thought of sort of like a row in a RDBMS. For each entry, there will be 1 or more attributes which are analogous to RDBMS columns. If you are interested in searching through LDAP for users will certain attributes, you may do so with search filters. In a search filter, you can use standard boolean logic to get a list of users matching an arbitrary constraint. Search filters are written in Polish notation AKA prefix notation.
Example:
(&(ou=Physics)(| (manager=cn=Freeman Dyson,ou=Physics,dc=Caltech,dc=edu) (manager=cn=Albert Einstein,ou=Physics,dc=Princeton,dc=edu) ))
When building LDAP queries in application code, you MUST escape any untrusted data that is added to any LDAP query. There are two forms of LDAP escaping. Encoding for LDAP Search and Encoding for LDAP DN (distinguished name). The proper escaping depends on whether you are sanitising input for a search filter, or you are using a DN as a username-like credential for accessing some resource.
Safe Java for LDAP escaping Example:
public String escapeDN (String name) {
//From RFC 2253 and the / character for JNDI
final char[] META_CHARS = {'+', '"', '<', '>', ';', '/'};
String escapedStr = new String(name);
//Backslash is both a Java and an LDAP escape character,
//so escape it first escapedStr = escapedStr.replaceAll("\\\\\\\\","\\\\\\\\");
//Positional characters - see RFC 2253
escapedStr = escapedStr.replaceAll("\^#","\\\\\\\\#");
escapedStr = escapedStr.replaceAll("\^ | $","\\\\\\\\ ");
for (int i=0 ; i < META_CHARS.length ; i++) {
escapedStr = escapedStr.replaceAll("\\\\" + META_CHARS[i],"\\\\\\\\" + META_CHARS[i]);
}
return escapedStr;
}
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Java Data Types: A Comprehensive Guide
Java, one of the most widely used programming languages, is known for its portability, security, and rich set of features. At the core of Java programming are data types, which define the nature of data that can be stored and manipulated within a program. Understanding data types is crucial for effective programming, as they determine how data is stored, how much memory it occupies, and the operations that can be performed on that data.
What are Data Types?
In programming, data types specify the type of data that a variable can hold. They provide a way to classify data into different categories based on their characteristics and operations. Java categorizes data types into two main groups:
1. Primitive Data Types
2. Reference Data Types
Why Use Data Types?
1. Memory Management: Different data types require different amounts of memory. By choosing the appropriate data type, you can optimize memory usage, which is particularly important in resource-constrained environments.
2. Type Safety: Using data types helps catch errors at compile time, reducing runtime errors. Java is a statically typed language, meaning that type checks are performed during compilation.
3. Code Clarity: Specifying data types makes the code more readable and understandable. It allows other developers (or your future self) to quickly grasp the intended use of variables.
4. Performance Optimization: Certain data types can enhance performance, especially when dealing with large datasets or intensive calculations. For example, using int instead of long can speed up operations when the range of int is sufficient.
5. Defining Operations: Different data types support different operations. For example, you cannot perform mathematical operations on a String data type without converting it to a numeric type.
When and Where to Use Data Types?
1. Choosing Primitive Data Types:
Use int when you need a whole number without a decimal, such as counting items.
Use double for fractional numbers where precision is essential, like financial calculations.
Use char when you need to store a single character, such as a letter or symbol.
Use boolean when you need to represent true/false conditions, like in conditional statements.
2. Choosing Reference Data Types:
Use String for any textual data, such as names, messages, or file paths.
Use Arrays when you need to store multiple values of the same type, such as a list of scores or names.
Use Custom Classes to represent complex data structures that include multiple properties and behaviors. For example, a Car class can encapsulate attributes like model, year, and methods for actions like starting or stopping the car.
1. Primitive Data Types
Primitive data types are the most basic data types built into the Java language. They serve as the building blocks for data manipulation in Java. There are eight primitive data types:
Examples of Primitive Data Types
1. Byte Example
byte age = 25; System.out.println(“Age: ” + age);
2. Short Example
short temperature = -5; System.out.println(“Temperature: ” + temperature);
3. Int Example
int population = 1000000; System.out.println(“Population: ” + population);
4. Long Example
long distanceToMoon = 384400000L; // in meters System.out.println(“Distance to Moon: ” + distanceToMoon);
5. Float Example
float pi = 3.14f; System.out.println(“Value of Pi: ” + pi);
6. Double Example
double gravitationalConstant = 9.81; // m/s^2 System.out.println(“Gravitational Constant: ” + gravitationalConstant);
7. Char Example
char initial = ‘J’; System.out.println(“Initial: ” + initial);
8. Boolean Example
boolean isJavaFun = true; System.out.println(“Is Java Fun? ” + isJavaFun);
2. Reference Data Types
Reference data types, unlike primitive data types, refer to objects and are created using classes. Reference data types are not defined by a fixed size; they can store complex data structures such as arrays, strings, and user-defined classes. The most common reference data types include:
Strings: A sequence of characters.
Arrays: A collection of similar data types.
Classes: User-defined data types.
Examples of Reference Data Types
1. String Example
String greeting = “Hello, World!”; System.out.println(greeting);
2. Array Example
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; System.out.println(“First Number: ” + numbers[0]);
3. Class Example
class Car { String model; int year;
Car(String m, int y) { model = m; year = y; } }
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Car car1 = new Car(“Toyota”, 2020); System.out.println(“Car Model: ” + car1.model + “, Year: ” + car1.year); } }
Type Conversion
In Java, type conversion refers to converting a variable from one data type to another. This can happen in two ways:
1. Widening Conversion: Automatically converting a smaller data type to a larger data type (e.g., int to long). This is done implicitly by the Java compiler.
int num = 100; long longNum = num; // Widening conversion
2. Narrowing Conversion: Manually converting a larger data type to a smaller data type (e.g., double to int). This requires explicit casting.
double decimalNum = 9.99; int intNum = (int) decimalNum; // Narrowing conversion
Conclusion
Understanding data types in Java is fundamental for effective programming. It not only helps in managing memory but also enables programmers to manipulate data efficiently. Java’s robust type system, consisting of both primitive and reference data types, provides flexibility and efficiency in application development. By carefully selecting data types, developers can optimize performance, ensure type safety, and maintain code clarity.
By mastering data types, you’ll greatly enhance your ability to write efficient, reliable, and maintainable Java programs, setting a strong foundation for your journey as a Java developer.
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
your colour seperating program, I made something basically identical a few years ago in Python, would love to hear an in depth everything about it, especially how you made the spinning gif
Sorry for the delay I've been kinda busy. I also had various reasons I didn't want to share my code, but I've thought about a better/different way so here it goes (but for the time being I'm as far away from my computer as I possibly could)
I used processing, which is, as far as I remember, based on java but focused on visual media
Starting with the gif part, processing has the save() and saveFrame() methods that save the image displayed, and it also has the "movie maker" that allows you to make GIFs (and others but I don't remember)
I don't know about other languages but processing runs setup() when it starts and draw() every frame
In setup() I load an image as a PImage (processing's image data type like an array or string) and access it's pixel list. Using that I fill a 256x256x256 int array where every color corresponds to a place in the array. This 3d int array is filled with the amount of times each color appears
Lastly I use a log function to convert those numbers into the dot size
During draw() I run through this array and use the point() method to draw every dot (I can define a dot's color using stroke() and it's size using stroke weight() )
There are some optimisations I don't have the patience to explain at the moment
Processing has various render modes. I've made 3d images using the 2d render but I didn't want to repeat the feat (pov: you make 3d in 2d and then your teacher explains the existence of 3d to you). It also has the translate() that moves the origin and rotate(), rotateX() rotateY() and rotateZ() that allows you to rotate the image
I don't know how much you know about processing so sorry if you don't understand or if I'm explaining things you already know
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Java Convert String to int | TpointTech
In Java, you can convert a Java String to an int using the Integer.parseInt() or Integer.valueOf() method.
Example:
String str = "123"; int num = Integer.parseInt(str); // Converts String to int System.out.println(num); //
Output:
123
int num = Integer.valueOf(str); // Also converts String to int
Both methods work similarly, but valueOf() returns an Integer object, while parseInt() returns a primitive int.
#how to convert string to int in java#how to convert string to int in java example#how to convert a string to int in java#how to convert string to integer in java#convert string to int java#convert string to int in java#how can convert string to int in java#how to convert a string to integer in java#convert int to string in java#string to integer in java#java convert string to int#convert string to int#how to convert integer to string in java#string to int java
1 note
·
View note
Text
Từ Khóa: Static trong Java | Hiểu và Sử Dụng Hiệu Quả
Từ khóa static trong Java là một khái niệm quan trọng mà bất kỳ lập trình viên nào cũng cần nắm vững để viết mã hiệu quả và tối ưu. Từ khóa static được sử dụng để quản lý tài nguyên bộ nhớ, tăng hiệu suất chương trình và tạo ra các thành phần chung cho toàn bộ lớp. Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ khám phá ý nghĩa của static trong Java, cách sử dụng hiệu quả, các trường hợp áp dụng và một số lưu ý quan trọng.
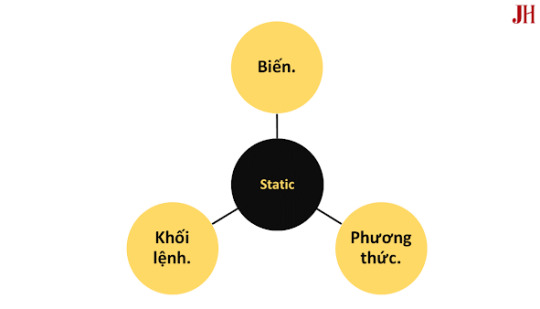
Ảnh mô tả các ngữ cảnh của từ khóa static.
Static trong Java là gì?
Trong ngôn ngữ lập trình Java, từ khóa static được sử dụng để chỉ định rằng một biến, phương thức hoặc khối mã thuộc về lớp (class) chứ không phải đối tượng (instance). Điều này có nghĩa là các thành phần static được chia sẻ giữa tất cả các đối tượng của lớp và không cần tạo đối tượng để truy cập chúng.
Ví dụ, khi bạn khai báo một biến static, tất cả các đối tượng của lớp sẽ sử dụng chung một bản sao của biến đó. Điều này giúp tiết kiệm bộ nhớ và đảm bảo tính nhất quán của dữ liệu. Từ khóa static thường được sử dụng trong các tình huống cần truy cập nhanh hoặc chia sẻ tài nguyên giữa các đối tượng.
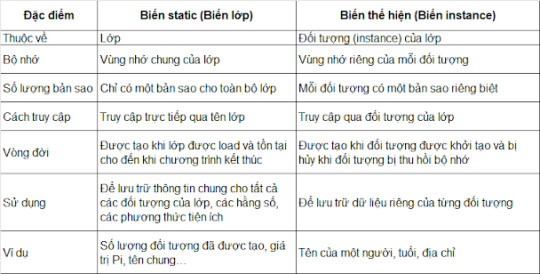
Sự khác biệt giữa biến static và biến instance
Các thành phần sử dụng static trong Java
1. Biến static (Static Variable)
Biến static (hay còn gọi là biến lớp) được khai báo với từ khóa static và thuộc về lớp, không thuộc về bất kỳ đối tượng cụ thể nào. Biến này được khởi tạo chỉ một lần khi lớp được nạp vào bộ nhớ và tồn tại trong suốt vòng đời của chương trình.
Ví dụ:
public class Counter { public static int count = 0; public Counter() { count++; } }
Trong ví dụ trên, biến static count sẽ tăng lên mỗi khi một đối tượng mới được tạo, và giá trị của nó được chia sẻ giữa tất cả các đối tượng.
2. Phương thức static (Static Method)
Phương thức static là các phương thức thuộc về lớp và có thể được gọi mà không cần tạo đối tượng. Chúng thường được sử dụng cho các tiện ích hoặc hàm không phụ thuộc vào trạng thái của đối tượng.
Ví dụ:
public class MathUtils { public static int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; } }
Bạn có thể gọi MathUtils.add(5, 3) mà không cần tạo một đối tượng của lớp MathUtils.
Lưu ý: Phương thức static chỉ có thể truy cập các biến hoặc phương thức static khác, không thể truy cập trực tiếp các thành phần không static của lớp.
3. Khối static (Static Block)
Khối static là một khối mã được thực thi chỉ một lần khi lớp được nạp vào bộ nhớ. Nó thường được sử dụng để khởi tạo các biến static hoặc thực hiện các tác vụ khởi tạo phức tạp.
Ví dụ:
public class DatabaseConfig { static String connectionString; static { connectionString = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb"; } }
Lợi ích của việc sử dụng static trong Java
Sử dụng từ khóa static mang lại nhiều lợi ích, bao gồm:
Tiết kiệm bộ nhớ: Vì các thành phần static chỉ được tạo một lần và chia sẻ giữa các đối tượng.
Truy cập nhanh: Không cần tạo đối tượng để sử dụng phương thức hoặc biến static, giúp mã đơn giản và hiệu quả hơn.
Quản lý tài nguyên chung: Các biến static là lựa chọn lý tưởng để lưu trữ dữ liệu dùng chung, chẳng hạn như biến đếm hoặc cấu hình hệ thống.
Khi nào nên sử dụng static trong Java?
Dù mạnh mẽ, static không phải lúc nào cũng là lựa chọn tối ưu. Dưới đây là một số trường hợp nên sử dụng static:
Khi bạn cần một biến hoặc phương thức dùng chung cho tất cả các đối tượng của lớp.
Khi viết các phương thức tiện ích (utility methods) như trong lớp Math hoặc Arrays của Java.
Khi cần khởi tạo dữ liệu ban đầu cho lớp bằng khối static.
Lưu ý: Việc lạm dụng static có thể dẫn đến khó khăn trong việc bảo trì mã, đặc biệt trong các ứng dụng lớn hoặc đa luồng. Ví dụ, biến static có thể gây ra vấn đề về đồng bộ hóa (synchronization) trong môi trường đa luồng.
Những sai lầm phổ biến khi sử dụng static trong Java
Sử dụng static cho mọi thứ: Lạm dụng static có thể làm mất đi tính hướng đối tượng của Java, khiến mã khó mở rộng.
Truy cập biến không static từ phương thức static: Điều này sẽ gây lỗi biên dịch vì phương thức static không thể truy cập trực tiếp các thành phần không static.
Bỏ qua vấn đề đồng bộ hóa: Trong môi trường đa luồng, các biến static cần được bảo vệ để tránh xung đột dữ liệu.
Để tránh những sai lầm này, hãy cân nhắc kỹ trước khi sử dụng static và đảm bảo rằng nó phù hợp với thiết kế của chương trình.
Mẹo sử dụng static trong Java hiệu quả
Sử dụng hằng số static final: Đối với các giá trị không thay đổi, hãy kết hợp static với final để tạo hằng số (constant). Ví dụ: public static final double PI = 3.14159;.
Kiểm tra tính thread-safe: Nếu sử dụng biến static trong môi trường đa luồng, hãy sử dụng các cơ chế đồng bộ hóa như synchronized hoặc các lớp trong gói java.util.concurrent.
Tổ chức mã rõ ràng: Đặt các phương thức và biến static vào các lớp tiện ích hoặc lớp cấu hình để tăng tính dễ đọc.
Kết luận
Hiểu và sử dụng từ khóa static trong Java một cách hiệu quả là kỹ năng quan trọng giúp lập trình viên tối ưu hóa mã nguồn, tiết kiệm tài nguyên và tăng hiệu suất chương trình. Từ khóa static mang lại sự linh hoạt trong việc quản lý tài nguyên chung, nhưng cần được sử dụng cẩn thận để tránh các vấn đề về bảo trì và đồng bộ hóa. Hy vọng bài viết này đã cung cấp cho bạn cái nhìn toàn diện về static trong Java và cách áp dụng nó vào các dự án thực tế.
Hãy tiếp tục thực hành và thử nghiệm với static trong các dự án của bạn để nắm vững hơn về cách nó hoạt động! Nếu bạn có bất kỳ câu hỏi nào về static trong Java, hãy để lại bình luận để chúng ta cùng thảo luận.
Bạn có biết cách dùng static trong Java đúng cách? Bài viết sẽ giúp bạn hiểu sâu và tránh lỗi phổ biến khi sử dụng từ khóa này. 🌐 Đọc thêm tại: Java Highlight | Website Học Lập Trình Java | Blogs Java
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Basics: A Comprehensive C Programming Language Tutorial for Beginners
Introduction
C programming language is often referred to as the backbone of modern programming. Developed in the early 1970s, C has influenced many other programming languages, including C++, Java, and Python. Its efficiency, flexibility, and powerful features make it a popular choice for system programming, embedded systems, and application development. This tutorial aims to provide beginners with a solid foundation in C programming, covering essential concepts, practical examples, and best practices to help you unlock the basics and start your programming journey.The
Why Learn C?
Before diving into the tutorial, it’s important to understand why learning C is beneficial:
Foundation for Other Languages: C serves as a stepping stone to learning other programming languages. Understanding C concepts will make it easier to grasp languages like C++, Java, and C#.
Performance and Efficiency: C is known for its speed and efficiency, making it ideal for system-level programming and applications where performance is critical.
Portability: C programs can be compiled and run on various platforms with minimal changes, making it a versatile choice for developers.
Rich Libraries: C has a vast collection of libraries that provide pre-written code for common tasks, speeding up the development process.
Strong Community Support: With decades of history, C has a large community of developers, providing ample resources, forums, and documentation for learners.
Getting Started with C Programming
1. Setting Up Your Development Environment
To start programming in C, you need to set up a development environment. Here’s how:
Choose a Compiler: Popular C compilers include GCC (GNU Compiler Collection) for Linux and MinGW for Windows. You can also use IDEs like Code::Blocks, Dev-C++, or Visual Studio.
Install the Compiler: Follow the installation instructions for your chosen compiler. Ensure that the compiler is added to your system’s PATH for easy access.
Choose a Text Editor or IDE: You can write C code in any text editor (like Notepad++ or Sublime Text) or use an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for a more user-friendly experience.
2. Writing Your First C Program
Let’s start with a simple "Hello, World!" program to familiarize you with the syntax:#include <stdio.h> int main() { printf("Hello, World!\n"); return 0; }
Explanation:
#include <stdio.h>: This line includes the standard input-output library, allowing you to use functions like printf.
int main(): This is the main function where the program execution begins.
printf("Hello, World!\n");: This line prints "Hello, World!" to the console.
return 0;: This indicates that the program has executed successfully.
3. Understanding C Syntax and Structure
C has a specific syntax that you need to understand:
Variables and Data Types: C supports various data types, including int, float, char, and double. You must declare variables before using them.
int age = 25; float salary = 50000.50; char grade = 'A';
Operators: C provides arithmetic, relational, logical, and bitwise operators for performing operations on variables.
Control Structures: Learn about conditional statements (if, else, switch) and loops (for, while, do-while) to control the flow of your program.
4. Functions in C
Functions are essential for organizing code and promoting reusability. Here’s how to define and call a function:#include <stdio.h> void greet() { printf("Welcome to C Programming!\n"); } int main() { greet(); // Calling the function return 0; }
5. Arrays and Strings
Arrays are used to store multiple values of the same type, while strings are arrays of characters. Here’s an example:#include <stdio.h> int main() { int numbers[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; char name[20] = "John Doe"; printf("First number: %d\n", numbers[0]); printf("Name: %s\n", name); return 0; }
6. Pointers
Pointers are a powerful feature in C that allows you to directly manipulate memory. Understanding pointers is crucial for dynamic memory allocation and data structures.#include <stdio.h> int main() { int num = 10; int *ptr = # // Pointer to num printf("Value of num: %d\n", *ptr); // Dereferencing the pointer return 0; }
7. Structures and Unions
Structures allow you to group different data types under a single name, while unions enable you to store different data types in the same memory location.#include <stdio.h> struct Student { char name[50]; int age; }; int main() { struct Student student1 = {"Alice", 20}; printf("Student Name: %s, Age: %d\n", student1.name, student1.age); return 0; }
Best Practices for C Programming
Comment Your Code: Use comments to explain complex logic and improve code readability.
Use Meaningful Variable Names: Choose descriptive names for variables and functions to make your code self-explanatory.
Keep Code Organized: Structure your code into functions and modules to enhance maintainability.
Test Your Code: Regularly test your code to catch errors early and ensure it behaves as expected.
Conclusion
Learning C programming is a rewarding journey that opens doors to various fields in software development. By following this comprehensive tutorial, you’ve unlocked the basics of C and gained the foundational knowledge needed to explore more advanced topics.
As you continue your programming journey, practice regularly, build projects, and engage with the C programming community. With dedication and persistence, you’ll become proficient in C programming and be well-equipped to tackle more complex challenges in the world of software development.
Ready to dive deeper? Explore advanced topics like memory management, file handling, and data structures to further enhance your C programming skills! Happy coding with Tpoint-Tech!
0 notes
Text
hi
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map;
public class FrequencyCounter { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {2, 3, 2, 5, 3, 2}; Map<Integer, Integer> frequencyMap = new HashMap<>(); for (int num : nums) { frequencyMap.put(num, frequencyMap.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1); } // Print the result for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : frequencyMap.entrySet()) { System.out.println("Number " + entry.getKey() + " appears " + entry.getValue() + " times."); } }
} ////////////////////
rray = [2, 1, 5, 1, 3, 2] target = 8 We’ll find the longest subarray where the sum is ≤ 8.
We use left, right, and sum to control and track the window .int left = 0, sum = 0, max = 0;
left: starting point of our sliding window
sum: running total of the current window
count: total number of valid subarrays we find
for (int right = 0; right < array.length; right++) { Expands the window by moving the right pointer forward. sum += array[right]; while (sum > target) { sum -= array[left]; left++; } max = Math.max(max, right - left + 1); }
/// Inheritance Inheritance allows a class to inherit fields and methods from another class. It supports code reuse and method overriding.
🔹 10. Polymorphism Polymorphism lets you perform the same action in different ways. It includes compile-time (overloading) and runtime (overriding) polymorphism.
🔹 11. Encapsulation Encapsulation binds data and methods together, hiding internal details. It’s achieved using private fields and public getters/setters.
🔹 12. Abstraction Abstraction hides complex implementation details and shows only the essentials. It’s achieved using abstract classes or interfaces.
List allows duplicates, Set allows only unique elements, Map stores key-value pairs. They are part of the Java Collections Framework f
Lambdas enable functional-style code using concise syntax. They simplify the implementation of functional interfaces.
🔹 19. Functional Interfaces A functional interface has exactly one abstract method. Examples include Runnable, Callable, and Comparator.
Stream API processes collections in a functional and pipeline-based way. It supports operations like filter(), map(), and collect()
Heap stores objects and is shared, while Stack stores method calls and local variables. Stack is thread-safe; Heap is managed by the garbage collector.
Immutable objects, like String, cannot be changed once created. They are thread-safe and useful in concurrent applications.
int left = 0, right = array.length - 1; while (left < right) { if (array[left] + array[right] == target) { // Found pair } else if (array[left] + array[right] < target) { left++; } else { right--; } } //////////////////
kafka partitions
List inputList = // input data Map uniqueMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Person person : inputList) { String key = person.name + "_" + person.age;if (!uniqueMap.containsKey(key)) { uniqueMap.put(key, person); // first time seeing this name+age } else {
///
List people = Arrays.asList( new Person("Alice", 30), new Person("Bob", 25), new Person("Charlie", 35) ); // Sort by age using lambda people.sort((p1, p2) -> Integer.compare(p1.getAge(), p2.getAge()));
////////////////
public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; }@Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (!(o instanceof Person)) return false; Person person = (Person) o; return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, age); }
}
/////////// hashCode() is used by hash-based collections like HashMap, HashSet, and Hashtable to find the bucket where the object should be placed.
bject.equals() method compares memory addresses
///
List people = Arrays.asList( new Person("Alice", 30), new Person("Bob", 25), new Person("Charlie", 35) ); // Sort by age using lambda people.sort((p1, p2) -> Integer.compare(p1.getAge(), p2.getAge())); // Print sorted list people.forEach(System.out::println); }
///
0 notes
Text
java- single constructor Vs multiple constructors
❌ The Multiple Constructor Example
public class Human {
private String name;
private int limbs;
private String skinColor;
public Human(String name) {
this(name, 4, "Unknown"); // Magic numbers!
}
public Human(String name, int limbs) {
this(name, limbs, "Unknown");
}
Why this fails: Hidden assumptions (Why default limbs = 4?), duplicate validation (What if limbs < 0?), brittle maintenance (Adding bloodType breaks all constructors)
✅ The Single Constructor Solution
public class Human {
private final String name; // Required
private final int limbs; // Required
private final String skinColor; // Required
public Human(String name, int limbs, String skinColor) {
Objects.requireNonNull(name);
if (limbs < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Limbs cannot be negative");
this.name = name;
this.limbs = limbs;
this.skinColor = skinColor;
}
}
benefits: No magic defaults -Forces explicit values, validation in one place - Fail fast principle, immutable by design - Thread-safe and predictable
Handling Optional Fields: The Builder Pattern For complex cases (like optional eyeColor), use a Builder:
Human britta = new Human.Builder("Britta", 4)
.skinColor("dark")
.eyeColor("blue")
.build();
Why Builders win: Clear defaults (`.skinColor("dark")` vs. constructor overloading), flexible (Add new fields without breaking changes), readable (Named parameters > positional args)
When Multiple Constructors Make Sense
Simple value objects (e.g., Point(x, y)), framework requirements (JPA/Hibernate no-arg constructor), most classes need just one constructor. Pair it with: factory methods for alternative creation logic and builders for optional parameters
This approach eliminates: hidden defaults, validation duplication and maintenance nightmares Do you prefer single or multiple constructors? Have you been bitten by constructor overload? Share your war stories in the comments!
#Java #CleanCode #OOP #SoftwareDevelopment #Programming
1 note
·
View note
Text
AFOS BASIC - primitive data types
To start simple I will only adopt four primitive data types.
byte - represented by the byte in JAVA (8bit signed)
integer - represented by the int in JAVA (32bit signed)
float - represented by float in JAVA
string - represented by the string in JAVA
Variable declaration is as follows:
[static] Var [shared] symbolname = expression[, symbolname = expression]
I will try to follow FreeBasic syntax as much as I can. This means datatype is autodetected (as opposed to explicitly declared). FreeBasic uses the Cast keyword to explicitly declare a datatype.
0 notes
Text
🔰 Starting out in Java? You’ve probably seen this line over and over: public static void main(String[] args) { // your code here } But did you know Java allows several valid variations of the main method? Let’s break it down for clarity! 👇 ✅ 𝑽𝒂𝒍𝒊𝒅 𝒎𝒂𝒊𝒏 𝑴𝒆𝒕𝒉𝒐𝒅 𝑺𝒚𝒏𝒕𝒂𝒙𝒆𝒔: 1️⃣ public static void main(String[] args) → Standard & most widely used 2️⃣ public static void main(String args[]) → Old-school array syntax (still valid) 3️⃣ public static void main(String... args) → Uses varargs — flexible and works the same 4️⃣ public static void main(String[] myCustomName) → Parameter name can be anything! ❌ 𝙄𝙣𝙫𝙖𝙡𝙞𝙙 𝙎𝙮𝙣𝙩𝙖𝙭𝙚𝙨: 🚫 public void main(String[] args) → Missing static 🚫 static void main(String[] args) → Missing public 🚫 public static void main(int[] args) → Wrong parameter type 🔎 The JVM specifically looks for: public static void main(String[] args) 🧠 𝙁𝙪𝙣 𝙁𝙖𝙘𝙩: You can overload the main method, but only the correct one (String[] args) will run by default! 📚 𝗡𝗲𝘄 𝘁𝗼 𝗝𝗮𝘃𝗮? Check out my full beginner-friendly blog post on this topic: 👉 https://wp.me/paNbWh-2l 💬 Got any Java tricks you wish you knew earlier? Drop them below 👇 Let’s grow together. #Java #100DaysOfCode #FullStackDevelopment #CodingJourney #LinkedInLearning #Beginners
#app development#backend#beginner#code like a pro#core java#datastructures#day1 of java#day2 of java#different type of main method#different type of main method in Java#frontend#fullst#fullstack#fullstackdeveloper#Java#main methods#output#print#programming
0 notes
Text
Optimize Letter Counting in Java Arrays
public class CountLettersInArray { 2 /** Main method */ 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // Declare and create an array 5 char[] chars = createArray(); 6 7 // Display the array 8 System.out.println("The lowercase letters are:"); 9 displayArray(chars); 10 11 // Count the occurrences of each letter 12 int[] counts = countLetters(chars); 13 14 // Display counts 15…

View On WordPress
0 notes